CBCT Scan For Oral Pathology
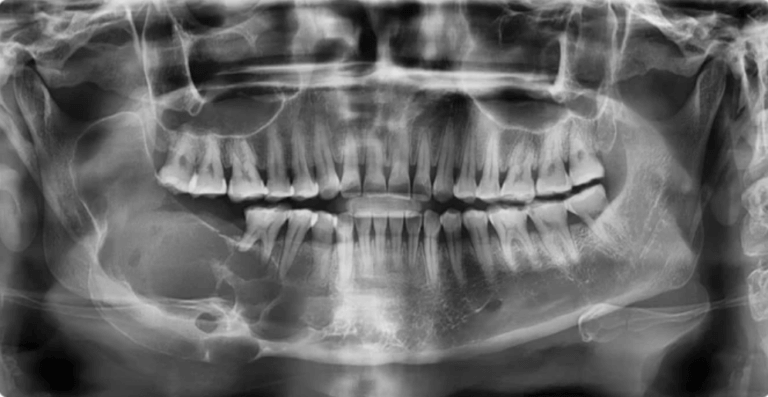
In the realm of dentistry, the integration of technology has revolutionized diagnostic approaches, particularly in the field of oral pathology. Among the array of diagnostic tools available, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) stands out as a powerful imaging modality, offering detailed three-dimensional views of the oral and maxillofacial region. As dental professionals strive for precise diagnoses and effective treatment planning, understanding the pivotal role of CBCT scans in oral pathology becomes paramount.
Before you deciding on whether a CBCT Scan for Oral Pathology is right for you, there are some things you should know:
Table of Contents
If you have any further questions about CBCT Scans at Oral Radiology Toronto, please contact us.
What Are CBCT Scans?
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a revolutionary x-ray imaging technology, providing three-dimensional views of the patient’s dental anatomy, including teeth, bones, nerves, and surrounding tissues. Unlike traditional two-dimensional X-rays, CBCT captures high-resolution, cross-sectional images by utilizing a cone-shaped beam of ionizing radiation.
The result is a detailed and accurate representation that enables dental professionals to assess anatomical structures with precision, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s oral health. CBCT scans play a crucial role in oral pathology, allowing dental professionals to diagnose and effectively treat diseases, abnormalities, and conditions affecting the oral and maxillofacial region.
What Is Oral Pathology?
Oral pathology encompasses the study and diagnosis of diseases, abnormalities, and conditions affecting the oral and maxillofacial region. This field of dentistry investigates a wide range of issues, including infections, tumors, cysts, developmental abnormalities, and inflammatory conditions that can impact oral health. Oral pathologists utilize various diagnostic tools and techniques, including clinical examination, imaging modalities like CBCT scans, and histopathological analysis of tissue samples, to identify and characterize these conditions accurately. Understanding oral pathology is crucial for dental professionals to provide timely intervention and appropriate management strategies to maintain or restore oral health and overall well-being for their patients.
What Are Different Types Of Oral Pathology That Can Be Imaged In CBCT?
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is an invaluable imaging modality for visualizing various types of oral pathology with exceptional detail and precision. Some of the oral pathology conditions that can be effectively imaged using CBCT include:
- Dental Caries: CBCT scans can reveal early signs of dental decay, enabling dentists to detect cavities in their early stages before they become visible on traditional dental X-rays.
- Periodontal Disease: CBCT imaging provides detailed views of the alveolar bone and periodontal structures, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of periodontal disease progression and bone loss.
- Endodontic Pathology: CBCT scans are instrumental in identifying periapical lesions, apical periodontitis, periapical abscesses, and other endodontic conditions that affect the dental pulp and periapical tissues.
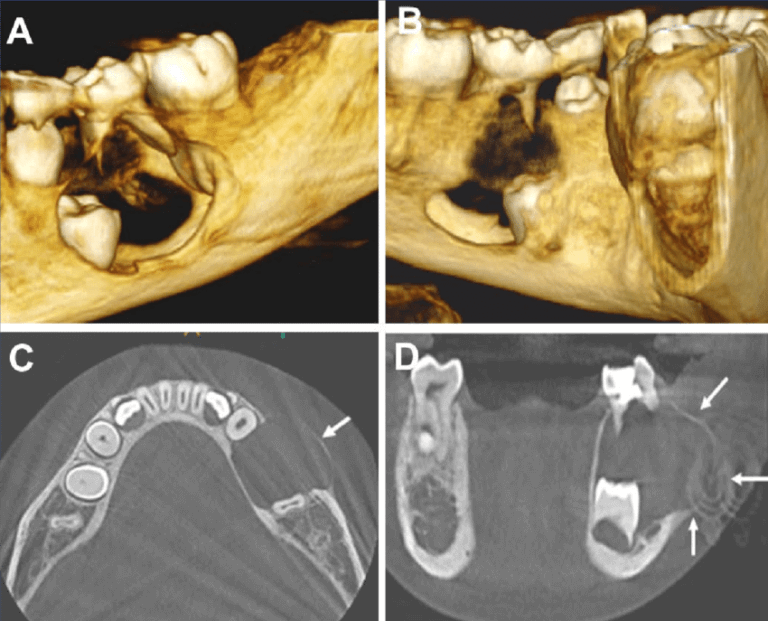
- Cysts: Oral cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pouches that can develop in various regions of the oral cavity and jawbone. CBCT imaging provides detailed three-dimensional views that aid in the identification and assessment of different types of oral cysts. The five most common types of cysts in the oral and maxillofacial region include radicular cysts associated with non-vital teeth, dentigerous cysts often related to impacted third molars, odontogenic keratocysts commonly found in the posterior mandible, nasopalatine duct cysts located in the midline of the palate, and globulomaxillary cysts typically situated between the roots of the maxillary lateral incisor and canine.
- Tumors: Oral tumors encompass a broad spectrum of neoplastic growths, ranging from benign to malignant. CBCT imaging is instrumental in evaluating the extent, size, and location of these tumors, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning. Benign tumors such as ameloblastomas or fibromas may present as well-defined radiolucencies or mixed radiopaque-radiolucent lesions. Malignant tumors, such as oral squamous cell carcinoma, may manifest as destructive lesions with irregular margins and evidence of bone invasion on CBCT scans. Additionally, CBCT can assist in assessing the involvement of adjacent structures, such as the mandibular canal or maxillary sinus, which is crucial for surgical planning and determining the prognosis.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: CBCT scans offer detailed visualization of the TMJ anatomy, allowing for the assessment of joint morphology, condylar position, and the presence of degenerative changes or pathology associated with TMJ disorders.
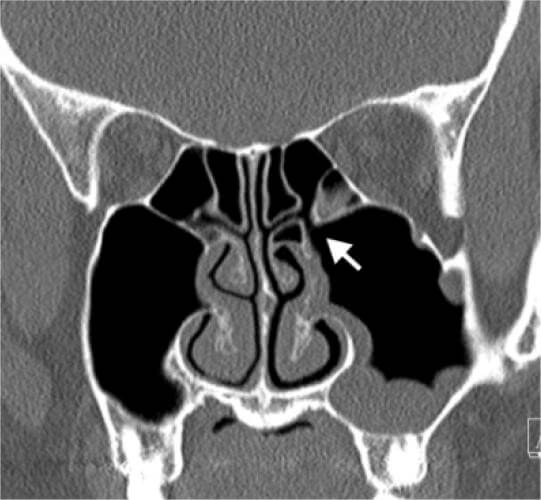
- Sinus Pathology: CBCT imaging provides comprehensive views of the paranasal sinuses, aiding in the diagnosis of sinusitis, sinus cysts, mucous retention cysts, and other sinus-related pathology that may impact dental treatment planning.
- Craniofacial Anomalies: CBCT scans are valuable for evaluating craniofacial anomalies such as cleft lip and palate, craniosynostosis, and other developmental abnormalities affecting the maxillofacial region.
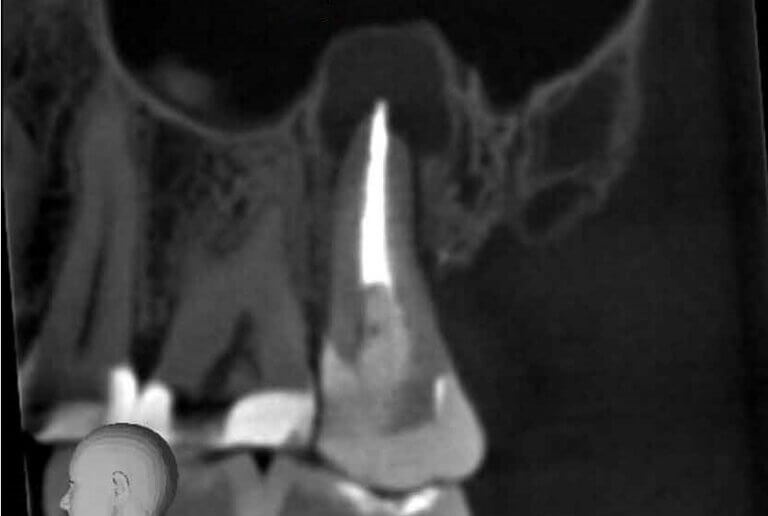
- Impacted Teeth: CBCT imaging assists in the identification and assessment of impacted teeth, including impacted third molars (wisdom teeth), canines, and supernumerary teeth, helping guide treatment decisions regarding extraction or orthodontic intervention.
By providing detailed three-dimensional images of the oral and maxillofacial region, CBCT technology enhances diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning, and patient outcomes in the management of various oral pathology conditions.
Why Do I Need A CBCT Scan For Oral Pathology?
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans are essential for oral pathology due to their ability to provide detailed three-dimensional imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region.
- Detailed three-dimensional imaging capability: CBCT scans provide comprehensive views of the oral and maxillofacial region, allowing for detailed visualization of structures in three dimensions.
- Superior visualization compared to traditional two-dimensional radiographs: CBCT offers higher resolution and clarity, enabling better identification and characterization of oral pathologies.
- Accurate detection and characterization of various oral pathologies: CBCT imaging aids in the precise diagnosis of conditions such as cysts, tumors, infections, and developmental abnormalities.
- Precise assessment of spatial relationships between lesions and surrounding anatomical structures: CBCT scans help clinicians understand the exact location and extent of oral pathologies in relation to adjacent tissues, vital structures, and anatomical landmarks.
- Aid in treatment planning, minimizing risks during surgical interventions: CBCT technology allows for careful preoperative planning, reducing the likelihood of complications during surgical procedures by providing detailed anatomical information and facilitating precise treatment protocols.
- Reduction in the need for invasive procedures: By providing comprehensive information about the nature and extent of oral pathologies, CBCT scans can help avoid unnecessary exploratory surgeries or invasive diagnostic procedures.
- Facilitation of comprehensive evaluation of complex cases: CBCT imaging is particularly valuable for assessing complex cases involving multiple dental and craniofacial issues, allowing for thorough evaluation and treatment planning.
- Improved diagnostic accuracy leading to better patient outcomes: With its ability to offer detailed and accurate imaging, CBCT contributes to more precise diagnoses, optimal treatment planning, and ultimately improved outcomes for patients undergoing oral pathology evaluation and treatment.
The utilization of CBCT scans in oral pathology offers numerous advantages, including superior imaging quality, precise anatomical localization, comprehensive evaluation of complex cases, and improved treatment planning. By harnessing the power of advanced imaging technology, dental professionals can deliver more accurate diagnoses, minimize risks, and optimize patient care, ultimately leading to better oral health outcomes for their patients.
How Much Does A CBCT Scan Cost For Oral Pathology?
At Oral Radiology Toronto, we provide quick and convenient dental CBCT scans for busy dentists and patients in the Toronto area. Our CBCT scans are useful for assessing the teeth, their supporting structures, the mandible and maxilla up to the floor of the nose.
Our competitively priced dental CBCT scans are professionally reviewed and interpreted by a Canadian licensed Oral Radiologist.
Prices are based on the size of CBCT volume:
- Small Field CBCT (most dental cases; 5x5cm): $234
- Medium Field CBCT : $315.90
- Large Field CBCT (8x8cm): $399
- Panoramic X-Ray: $84
Normal CBCT report turnaround time is up to 10 business days. Expedited reporting (2 business days) is an extra $50.
Please note that we do NOT offer field of views larger than 8x8cm or imaging of structures outside the maxilla and mandible, such as the temporomandibular joints, paranasal sinuses, the cervical spine, the neck and the airway spaces (i.e. craniofacial CT scan).
How Do I Get A CBCT Scan For Oral Pathology?
- For Referring Dentists: Refer a dental patient for a CBCT Scan using our Online Referral Form.
- For Dental Patients: Schedule a CBCT scan visit at Oral Radiology Toronto using our Online Appointment Booking System.
