CBCT Scan For Dental Cysts
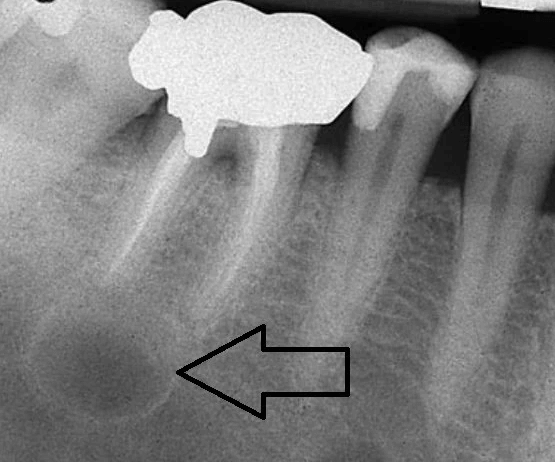
Dental cysts, though often asymptomatic, can pose significant risks to oral health if left untreated. These fluid or semi-fluid-filled sacs can develop in the gums, roots of teeth, or jawbones, and their detection and management are crucial for preventing potential complications such as infections and bone damage. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans have emerged as a powerful diagnostic tool in dentistry, offering detailed three-dimensional images that provide invaluable insights into the presence, size, and location of dental cysts.
Before you deciding on whether a CBCT Scan for Dental Cysts is right for you, there are some things you should know:
Table of Contents
If you have any further questions about CBCT Scans at Oral Radiology Toronto, please contact us.
What Are CBCT Scans?
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a revolutionary x-ray imaging technology, providing three-dimensional views of the patient’s dental anatomy, including teeth, bones, nerves, and surrounding tissues. Unlike traditional two-dimensional X-rays, CBCT captures high-resolution, cross-sectional images by utilizing a cone-shaped beam of ionizing radiation.
The result is a detailed and accurate representation that enables dental professionals to assess anatomical structures with precision, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s oral health. CBCT scans provide unparalleled insights into the size, location, and relationship of cystic lesions to adjacent structures, enabling dentists to formulate precise treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs.
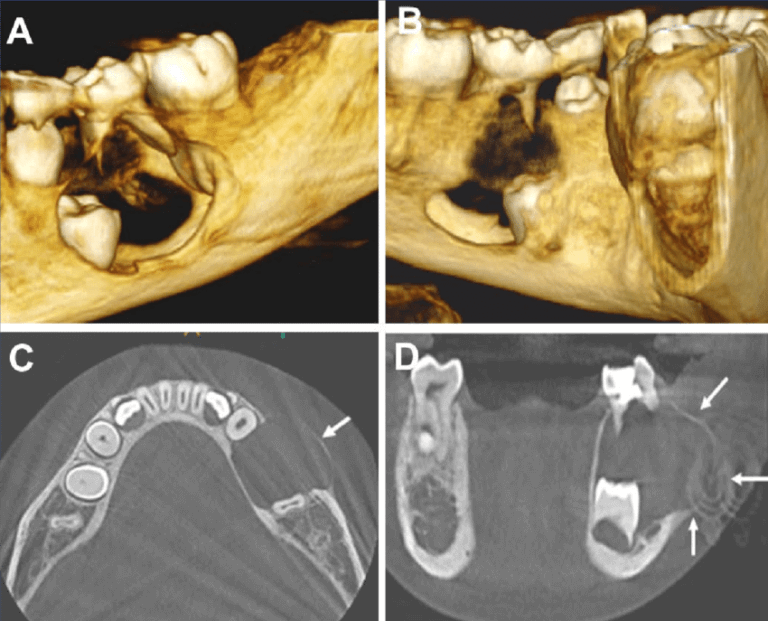
What Are Dental Cysts?
Dental cysts are abnormal, fluid-filled sacs that can develop within the oral cavity, particularly in the gums, roots of teeth, or jawbones. These cysts typically arise from various causes, including infection, inflammation, or developmental abnormalities within the dental tissues. While some dental cysts may remain asymptomatic and go unnoticed for extended periods, others can cause discomfort, swelling, or even lead to serious complications if left untreated. There are several types of dental cysts, each with distinct characteristics and origins. Regardless of their type, prompt detection and management of dental cysts are essential to prevent complications such as infection, bone loss, or damage to adjacent teeth.
What Are Different Types Of Dental Cysts?
Odontogenic cysts are cystic lesions that originate from the tissues involved in tooth development. These cysts can vary in size, location, and clinical behavior, and they are classified based on their histopathological features and etiology. Some of the most common types of odontogenic cysts include:
- Radicular Cysts (Apical Cysts): Radicular cysts are the most prevalent odontogenic cysts and typically develop at the apex (tip) of a tooth’s root. They arise as a result of inflammation or infection within the pulp tissue, leading to the formation of a cystic sac. Radicular cysts are often associated with non-vital (dead) teeth and can cause bone destruction if left untreated.
- Dentigerous Cysts (Follicular Cysts): Dentigerous cysts are cysts that form around the crown of an unerupted tooth, typically associated with impacted third molars (wisdom teeth) or canines. These cysts develop from the follicle surrounding the developing tooth and can cause displacement of adjacent teeth and resorption of bone.
- Odontogenic Keratocysts (OKCs): Odontogenic keratocysts (OKCs) are aggressive cystic lesions characterized by a lining of stratified squamous epithelium. These cysts have a high recurrence rate and can exhibit rapid growth, leading to significant bone destruction and displacement of teeth. OKCs often require extensive surgical management to prevent recurrence.
- Lateral Periodontal Cysts: Lateral periodontal cysts are relatively uncommon odontogenic cysts that arise from the periodontal ligament adjacent to the roots of teeth. These cysts are typically small and asymptomatic but may require surgical removal if they cause discomfort or compromise oral health.
- Calcifying Odontogenic Cysts (Gorlin Cysts): Calcifying odontogenic cysts, also known as Gorlin cysts, are rare lesions that may exhibit calcifications within the cystic lining. These cysts can present with variable clinical and radiographic features and may mimic other odontogenic tumors, necessitating careful diagnosis and management.
Understanding the different types of odontogenic cysts is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans play a crucial role in the evaluation of these cysts, providing detailed three-dimensional images that aid in differential diagnosis and surgical treatment guidance. In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into the diagnostic utility of CBCT scans for odontogenic cysts and explore their role in improving patient outcomes.
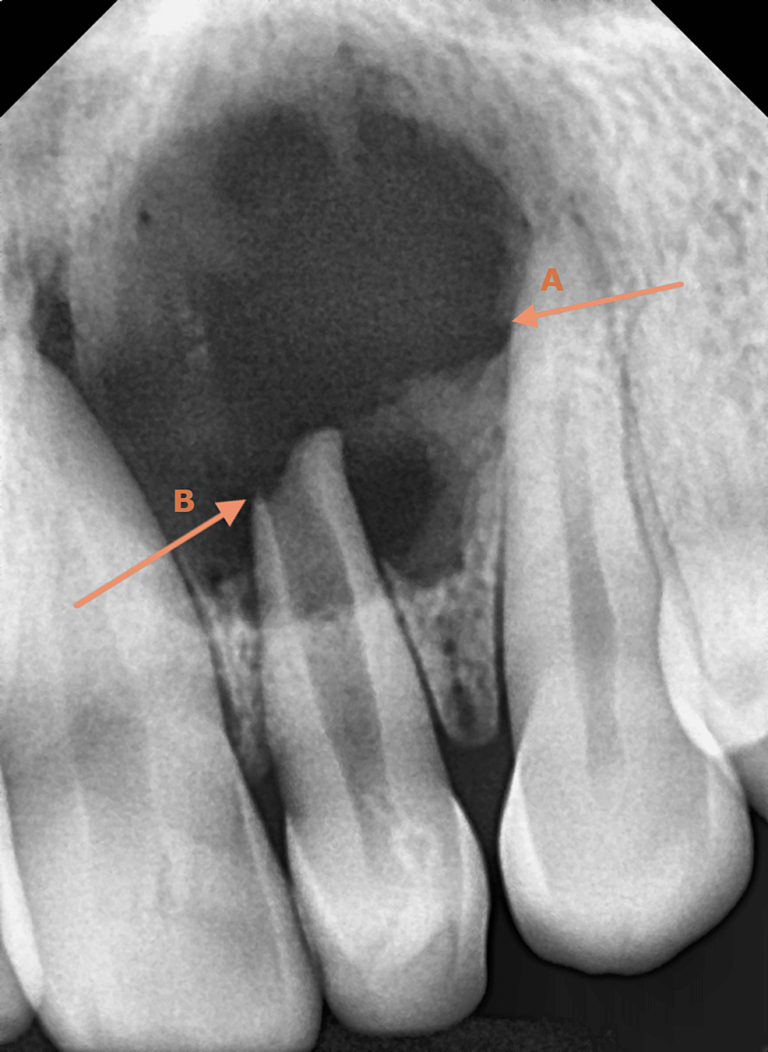
Why Do I Need A CBCT Scan For Dental Cysts?
While traditional dental imaging techniques such as intraoral and panoramic X-rays are valuable for routine examinations, they often provide limited information when it comes to diagnosing and evaluating dental cysts. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans offer several distinct advantages that make them indispensable in the assessment of dental cysts:
- Detailed 3D Visualization: CBCT scans provide high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the oral and maxillofacial structures, offering unparalleled detail compared to conventional X-rays. This detailed visualization allows dentists to accurately assess the size, shape, and location of dental cysts, as well as their relationship to surrounding anatomical structures such as teeth, nerves, and sinuses.
- Comprehensive Assessment: CBCT scans enable comprehensive evaluation of dental cysts by capturing images from multiple angles. Dentists can examine the cystic lesion from various perspectives, gaining a comprehensive understanding of its extent and morphology. This thorough assessment is essential for planning appropriate treatment strategies and predicting potential complications.
- Precise Treatment Planning: With CBCT scans, dentists can precisely plan the surgical management of dental cysts. By visualizing the exact location and size of the cystic lesion in three dimensions, clinicians can determine the optimal approach for cyst removal while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This precision enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes and reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
- Differential Diagnosis: CBCT scans aid in distinguishing dental cysts from other pathological conditions that may present with similar radiographic features. By examining the internal structure and density of the cystic lesion, dentists can differentiate between cystic lesions, tumors, or inflammatory processes, facilitating accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment selection.
- Monitoring Disease Progression: CBCT scans are invaluable for monitoring the progression of dental cysts over time. By comparing sequential scans, dentists can track changes in cyst size, morphology, and surrounding bone integrity, enabling early detection of recurrence or complications. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention and management adjustments as needed.
In summary, CBCT scans are indispensable for the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of dental cysts. Their ability to provide detailed three-dimensional images facilitates precise treatment planning, differential diagnosis, and long-term monitoring, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enhancing oral health care delivery.
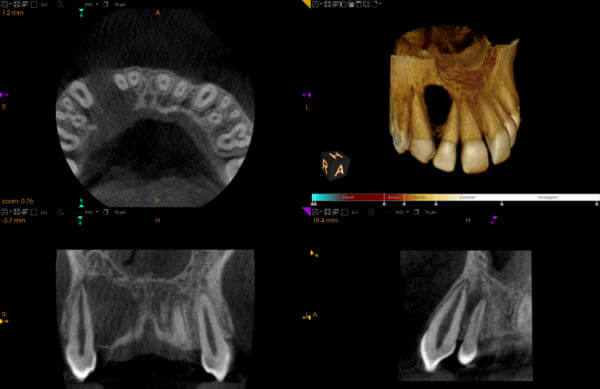
What Do Odontogenic Cysts Look Like In CBCT Scans?
Odontogenic cysts exhibit various radiographic appearances in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans, depending on their type, size, and location. While some cysts may present with well-defined borders and homogeneous radiolucency, others may display irregular margins or internal septations. Here are some common characteristics of odontogenic cysts as seen in CBCT scans:
- Radiolucency: Odontogenic cysts typically appear as radiolucent (dark) lesions on CBCT scans due to their fluid-filled nature. The extent and density of radiolucency may vary depending on factors such as cyst size, composition, and surrounding bone density.
- Margins: The margins of odontogenic cysts in CBCT scans can range from well-defined to irregular. Well-defined margins indicate a clear boundary between the cystic lesion and surrounding bone, facilitating accurate measurement and localization. Conversely, irregular margins may suggest cystic expansion or infiltration into adjacent tissues, potentially complicating surgical management.
- Internal Structure: Some odontogenic cysts may exhibit internal septations or trabeculations within the cystic cavity, which appear as fine lines or radiopaque areas on CBCT scans. These internal structures can provide valuable diagnostic clues regarding the cyst’s origin, growth pattern, and likelihood of recurrence.
- Adjacent Changes: Odontogenic cysts may cause changes in the surrounding bone density and morphology, which are visible on CBCT scans. These changes may include cortical thinning, bone expansion, or displacement of adjacent teeth. Assessment of these adjacent changes is essential for evaluating the cyst’s impact on surrounding structures and planning appropriate treatment.
- Location: The location of odontogenic cysts within the oral and maxillofacial region can vary, influencing their radiographic appearance on CBCT scans. Cysts located in proximity to vital structures such as nerves or sinuses may exhibit characteristic radiographic features that aid in differential diagnosis and treatment planning.
Understanding the radiographic appearance of odontogenic cysts in CBCT scans is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Dentists can utilize these imaging findings to assess cyst size, extent, and relationship to surrounding structures, enabling personalized and effective management strategies.
How Much Does A CBCT Scan Cost For Dental Cysts?
At Oral Radiology Toronto, we provide quick and convenient dental CBCT scans for busy dentists and patients in the downtown Toronto area. Our CBCT scans are useful for assessing the teeth, their supporting structures, the mandible and maxilla up to the floor of the nose.
Our competitively priced dental CBCT scans are professionally reviewed and interpreted by a Canadian licensed Oral Radiologist.
Prices are based on the size of CBCT volume:
- Small Field CBCT (most dental cases; 5x5cm): $227
- Medium Field CBCT : $306.45
- Large Field CBCT (8x8cm): $388.50
- Panoramic X-Ray: $82
Normal CBCT report turnaround time is up to 10 business days. Expedited reporting (2 business days) is an extra $50.
Please note that we do NOT offer field of views larger than 8x8cm or imaging of structures outside the maxilla and mandible, such as the temporomandibular joints, paranasal sinuses, the cervical spine, the neck and the airway spaces (i.e. craniofacial CT scan).
How Do I Get A CBCT Scan For Dental Cysts?
- For Referring Dentists: Refer a dental patient for a CBCT Scan using our Online Referral Form.
- For Dental Patients: Schedule a CBCT scan visit at Oral Radiology Toronto using our Online Appointment Booking System.
